Search
Product categories
Latest News
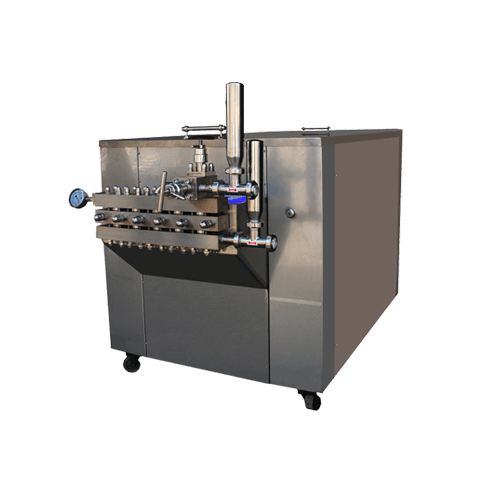
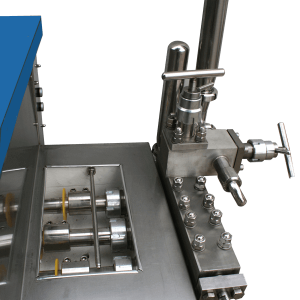
Homogenizer
technical specification:
| material: | steel |
|---|---|
| head | It has 2 heads and a three-piece block |
| Capacity | 1 ton to 10 tons |
| design | APV |
Please submit your comments about this product.
Homogenizer or homogenizer
What is a homogenizer
Radman single machine construction equipment that they use to provide the homogenizing power they need, called a homogenizer or homogenizer is said. Radman machine single homogenizer that is able to process liquid matrices at pressures between 20 and 100 MPa, for example milk homogenization, today in the dairy, pharmaceutical and cosmetic beverage industries mainly to reduce particle size and thus increase emulsion stability Are used to prevent creaming and coagulation phenomena.
Radman Machine Single Homogenizer is a laboratory or industrial equipment that is used to homogenize or homogenize different types of materials such as tissue, plant, food, soil, homogen Milk and many more are used. Many different models of homogenizers are produced using different physical technologies to create a disturbance that the type of homogenizer directly depends on the type of material as well as the intended application of the final product. Homogenization is usually done after pasteurization of milk.
What is homogenization
Homogenization is the process of breaking down a substance (gaseous, liquid, or solid) and mixing it into another substance (usually a liquid) that is called It does not normally combine with it like milk homogeneity. The word “ homogenize” or “homogenize” is used to describe the ability to create a one-handed substance from two insoluble or solid and liquid liquids.
Homogenization is a fluid mechanical process that involves splitting micron-sized particles to create a stable emulsion . Many industries use homogenization to facilitate more stable mixtures with better bioavailability, controlled consistency, and longer shelf life.
Types of homogenizers or single Radman machine homogenizers
Current homogenization processes or methods can be divided into three (3) main categories: mechanical, Ultrasonic and pressure divided in small hand size to homogenizers Large industrial size available.
Mechanical Homogenizers
Mechanical homogenizers can be divided into three separate categories:
1- Homogeneous rotor-stator instruments
The rotor-stator homogenizer consists of a metal shaft, or rotor, that rotates rapidly inside a fixed external chamber, or stator. This creates a suction effect so that the sample is drawn into the space between the two components. When a sample is processed through the machine, a rapidly rotating rotor pulls the sample upwards. It is then pressurized into a centrifuge by means of a stator with many small gaps .
A combination of rpm from the rotor and exit through the slits allows the specimen to be mechanically cut into very fine particles. Multiple variables can be optimized to increase process efficiency. These include sample size, rotor tip speed, processing time, and sample viscosity. These homogenizers are suitable for use in liquids and suspensions and for mixing or emulsions .
They can also be used for cell types to extract DNA and homogenize soft tissue. This process provides a fast and efficient approach for individual samples. Disadvantages of using probes mean that rotor-stator homogenizers are not suitable for high-consumption multi-sample applications.
Rotor-stator homogenizers transfer a moderate amount of heat to the sample, so you may have to cool the heat-sensitive samples. Rotor-stator homogenizers , originally designed to produce emulsions and dispersions, are highly efficient machines that, if used properly, produce high product performance and small particle sizes.
2- Blade type homogenizers and nut homogenizers
Blade Homogenizers
Blade homogenizers In contrast to rotor-stator homogenizers, blade homogenizers are relatively less selectable for use due to reduced efficiency . Blade homogenizers, also called blenders, have cutting blades that rotate rapidly to cut the sample. Although they can not reduce the particle size to the capacity of rotor-stator homogenizers, blade homogenizers can process different sample sizes.
Bead Mill Homogenizers
As the name implies, the nut mill homogenizer involves the use of a nut. The specimen is placed in a tube with the beads, then strongly stimulated. As a result of the movement of the beads and the collisions between them, the sample becomes homogeneous. The type of movement used to stir the nuts varies for different machines, but is usually done by violent shaking.
Several instances can be homogenized simultaneously, making this program suitable for high-power applications. Some applications include tissue breakdown and cell disruption. Nut mills can be used with dry samples so they can be suitable for milling or grinding solids.
One of the benefits of this homogenizer is the use of disposable tubes , which means that the possibility of contamination is greatly reduced. Different types of beads are available for different uses and expand the scope of potential application. Disadvantages of the nature of the process mean that laboratory mill homogenization on a laboratory scale is only suitable for small samples. A few grams or milliliters is the only thing you can process in a tube. Small amounts of bead material may get into your sample, which may be a concern for some applications.
3- Ultrasonic Homogenizer
The ultrasonic sound homogenizer includes a beep. The probe vibrates rapidly and transmits its ultrasonic energy to the surrounding material.
Ultrasonic homogenizers with high sound pressure waves combine materials and form microbubbles . These bubbles get bigger and bigger and eventually burst, causing intense heat. The ultrasonic process leads to the formation of cavities, which include the rapid formation and collapse of bubbles, which contributes to this phenomenon cavitation . The resulting wave
How does the homogenizer work?
Energy waves are dispersed in the fluid passing through the valve of the homogeneous device, producing turbulent vortices of the same average spherical diameter. Thus, blood cells are disrupted by these eddy currents, which reduce their average size.
Application of Radman Single Machine Homogenizer in Dairy and Juice Industries
Food homogenization is done by a mechanical device called a homogenizer. It is one of the oldest applications of homogenization in milk processing. Normally “standardization” (mixing milk from several different herds or farms to produce more consistent raw milk before processing) is done beforehand. The fat in milk is normally separated from the water and accumulates at the top.
The purpose of homogenization is to create a stable emulsion , such as milk homogeneity, so that fat globules do not accumulate to form a top layer of milk. Homogenization primarily disrupts fat cells in much smaller sizes, thereby reducing the formation of fat and cream in the milk head.
Homogenize milk to reduce the tendency of fats to bulge and shrink. Basically, all homogenized valves are produced mechanically. The valve passes through a small duct very quickly. Fat cell breakdown is caused by factors such as turbulence and bubbling.
Homogeneous milk reduces the size of a fat glob from an average diameter of 3.5 microns to less than 1 micrometer. This increases four to six times in Surface fat / plasma levels associated.
Materials and Methods Homogenizing or homogenizing milk is done by mixing a large amount of milk, and then applying milk pressure from small holes to the milk. Homogenization of milk is an essential tool in the milk food industry to create different levels of flavor and fat concentration.
Purpose of milk homogenization:
Prevents the formation of cream and fat coagulation in the milk head.
Homogeneity of milk increases the viscosity of milk and has a more beautiful appearance if used in coffee.
Homogeneous milk fat globules do not rise easily and there is no need to stir the milk before serving.
Milk homogeneity prevents fat burning and excessive irritation.
Homogeneity reduces whey, which means that when homogeneous milk coagulates, it creates a soft whey, because the milk tastes better due to its brighter appearance, heavier body and richer taste.
Milk is digestible due to the smaller number of fat globules and other parts. Due to the low curd stress, homogeneous milk can be recommended for infants.
Milk homogeneity reduces the chance of fat separation during the production of evaporated milk and ice cream, this makes you have a softer texture.
The homogenizer can be used to prepare reconstituted milk with a mixture of cream or skim milk, and the percentage of cream in the milk can be controlled.
Homogeneity of milk makes milk less exposed to the production of odor and taste of oxide.
Single-stage and two-stage homogenization
The Radman Machine Single Homogenizer may be equipped with a homogeneous device or two interconnected devices, hence the term single-stage homogenization and two-stage homogenization. The two-step system is shown in the figure below.
In both single-stage and two-stage homogenization methods, the total homogenization pressure (P 1 ) is used on the first device Becomes. In one-stage homogenization, the return pressure (P 2 ) is created by the process. In two-stage homogenization, the return pressure (P 2 ) is created by the second stage. In this case, the return pressure can be selected to achieve the desired homogenization efficiency.
Using modern Radman machine single devices, the best result is obtained when the relation (P 2 ) / (P 1 < / sub>) is about 0.2. The second stage also reduces the noise and vibrations in the outlet pipe. One-step homogenization may be used to homogenize high-fat products that require high viscosity (specific cluster formation). Two-stage homogenization is primarily used to achieve optimal homogenization results and breakdown of fat clusters in products with high fat content. The formation and decomposition of clusters is shown in the figure below.
Disorder of fat cells in the first and second stages of homogenization
Figure left after the first step
Figure right after the second step
Components of a homogenizer and each function
THE HIGH-PRESSURE PUMP
The product enters the pump block and is pressurized by the piston pump. The homogenizer consists of a high-pressure pump with an adjustable nozzle through which liquids are forced to pass at a very high pressure. The pressure obtained is determined by the return pressure resulting from the distance between the forcer (the means by which the liquid is pressurized in the pump) and the seat in the homogenizer. Always (P 1 ) homogenized pressure and (P 2 ) return pressure to the first stage.
The size of the fat globules decreases as it passes through this valve. In practice, most valves use a combination of three principles: shear, impact in the breakwater ring, and a sudden drop in pressure when the fluid leaves the valve cause homogenization of the material.
Homogeneity can occur due to cutting or due to disorder. The shear action occurs between the globules and in the narrow opening through which the milk is forced to pass. This disorder occurs in the breaker ring and is also due to a sudden drop in pressure as fluid exits the valve.
- This causes excessive viscosity, which sometimes results in a product that is very difficult to pump or cool. Among other factors, the size and shape of the openings are also affected by the volume of milk used per unit time and the viscosity of the product.
& nbsp;

- Mir Lang Crankcase
- Pistons
- Damper Modifier
- Pump block
- Homogenization device, first stage
- Homogenization device, second stage
- Main drive motor
- V-belt transmission
- Hydraulic pressure setting system
The piston pump is driven by a powerful electric motor, through belts and pulleys through a gearbox to the crankshaft and the transfer of the connecting rod, which converts the rotational motion. Slow motor causes reciprocating movement of pump pistons.
The piston pump is a positive pump and its capacity can only be adjusted by changing the engine speed or resizing the pulleys. To control higher pressures, pistons with smaller diameters are installed. This reduces the maximum capacity, because each size of device has a maximum crankshaft speed.
The larger device has a longer impact length or longer piston. In many cases the diameter of these pistons is also larger. A high pressure pump typically has three to five pistons operating on cylinders in a high pressure block. They are made of very durable materials.
Radman machine homogenizer has two sealed pistons. To lubricate the pistons, water is given to the space between the seals. A mixture of hot condensate and steam is also used for disinfection ( aseptic ) and killing microorganisms at the bottom of the homogenizer.
The piston pump always generates a vibrating current. Acceleration and deceleration of the fluid causes pressure in the suction pipe. To prevent the phenomenon of Cavitation Cavitation (a phenomenon in which rapid changes in pressure in a liquid leads to the formation of small holes full of steam in places where the pressure is relatively low and additional noise It is caused by shocks and vibrations and a significant reduction in efficiency because it fluctuates the flow pattern. There is a damper on the suction pipe to reduce vibration. On the outlet side, vibration and noise may occur, which is why the outlet pipe is also equipped with a damper.
The main components of Radman machine homogenization machine:
Homogeneous pump
Radman machine single homogeneous pump creates the desired pressure for homogenization
- It can be of different shapes and sizes.
- Most valves are of the pipette type with a ring breaker so that the liquid is perpendicular to the inner surface The cutting ring strikes and exits the opening formed by the valve and the conical position.
. • The valve is held by a heavy spring with adjustable tension. When liquid pressure is applied to it, the valve rises by a few thousandths of an inch, creating a narrow annular opening.
- Milk homogenization should be done at a pressure of 2000 to 3000 psi (136-204 kg / cm²)
. For milk with a maximum of 6% fat, 136-170 kg / cm2 (2000-2500 psi) in one step is usually sufficient.
. Excessive pressure may increase the tendency for the milk to close or thicken during cooking, as this increases the destabilizing effect on milk proteins.
. For products with more than 6% fat, two-step homogenization is required to prevent fat accumulation: 16-170 kg / cm2 in the first stage and 34 kg / cm2 in the second stage. .
Forcer
Shear forces in rotor-stator homogenization and hole forces in ultrasonic homogenization are created by this part in Radman’s single homogenizer.
Impact ring
Impact forces for homogenization of materials can be due to the impact between the material and other solid components such as nuts (in the homogenization of the nut mill) or the impact of high pressure current with the blade, plate Or loop done.
Seat position
Hydraulic actuator Hydraulic actuator
Components of a two-stage homogeneous device
The figure above shows the system of a hydraulic homogenizer . Piston pump, depending on the product, increases the valve pressure from about 300 kPa (3 times) at the inlet to a homogeneous pressure of 10-25 MPa (100-250 times). The pressure to the first stage before the machine (homogenization pressure) is automatically kept constant. The oil pressure on the hydraulic piston and the homogenization pressure on the Forcer (the device by which the liquid is pressed into the pump) balance each other. The hydraulic unit can adjust both the first and second stages to the desired pressure . Homogenization pressure is done by adjusting the oil pressure. The actual homogenization pressure is displayed on the barometer. Homogenization is always done in the first stage.
Homogenization in the second stage has basically two purposes:
- Provide constant and controlled return pressure to the first stage, create the best possible conditions for homogenization
- Cluster decomposition is formed directly after homogenization as shown in the figure below.
The valve is supplied to the space between the stand and the sucker with high pressure. The position of the position from the forser is approximately 0.1 mm or 100 times the size of the fat balls in the homogeneous milk. The fluid velocity is typically 100-400 m / s in a narrow annular slit. The higher the homogenization pressure, the higher the velocity.
Homogenization takes 10 to 15 microseconds. During this time, all the compressive energy delivered by the piston pump is converted to kinetic energy. Some of this energy is converted back into pressure after the device. The other part is released in the form of heat. Every 40 times the pressure drop on the device increases the temperature by 1 ° C. Less than 1% of energy is used for homogenization, but high-pressure homogenization is nevertheless the most efficient method available.
Homogenizer (homogenizer) Advantages and risks
Using Radman Single Machine Homogenization Equipment in the Food Industry has many benefits both for the industry itself and for the customers who receive the final results of the industry.
extend useful life
A little known advantage that homogenization offers is improved durability . The process of reducing particle size, along with other forces, requires the use of intense pressure. This pressure on food products often leads to more stable chemical structures. This will increase the freshness and durability of the final product.
Better food quality
The homogenization process also leads to higher food quality. Reducing the particle size of products leads to the production of a final product that has improved its taste, texture, appearance and overall quality compared to its heterogeneous samples
preserve food
Increased shelf life brought about by homogenization is one of the benefits of food preservation. While heat treatment is effective in preserving food and killing harmful bacteria and microorganisms , heat can also kill beneficial microorganisms, vitamins and nutrients. Homogenization, on the other hand, uses pressure to do the same and slightly more destructive task. This leads to a healthier diet.
You may be wondering, “What would be the danger if I drank non-homogenized milk?” The answer to this question is “no”. Homogenization has no known health benefits. Non-homogenization is not necessarily raw milk (“raw” means not pasteurized). Although raw milk is heterogeneous, not all non-homogeneous milks are raw.
The effect of homogenization on the physical structure of milk has many advantages:
Smaller fat globules do not cause cream to form on the milk head.
Whiter and more appetizing color
Oxidation reduction
More suitable aroma and flavor
However, homogenization also has certain disadvantages:
Some increase in sensitivity to light – sunlight and radiation that can lead to “special flavor” in pasteurized milk products.
. This milk may not be suitable for making semi-hard or hard cheeses because it has no ability to clot or clot.
Homogenization is a mechanical treatment of fat globules in milk caused by the passage of milk under high pressure through a small hole, which reduces the average diameter and increases the number and The surface becomes fat cells. Homogeneous milk is dangerous for your health. Homogenized milk has smaller particles than non-homogeneous milk. As a result, during digestion, fine particles are absorbed directly by the bloodstream, thus harming your health. Homogenized milk is also known to cause cancer and heart disease
High and Ultra High Pressure Homogenization
Potential and applications of high and ultra-high pressure homogenization for inactivation of pathogenic species in laboratory and food systems except the main application of homogenization for stabilization of food and dairy emulsions Is known.
High and Ultra High Pressure Homogenization guarantees the destruction of microorganisms in liquid food products and has a positive effect on It has food stability. This method has the least effect on the nutritional value and sensory properties of processed liquids.
UHPH technology has reduced the efficiency of particles compared to classical homogenization, and its positive effect is the result of several mechanisms such as sudden pressure drop, torsional and shear stresses, turbulence, clogging, cavitation phenomena Shock waves and temperature increase coincide with decrease.
Today, advances have been made in the use of high-pressure homogenizer (HPH) to reduce microbial load or modulate the activity of some enzymes. But the final effect of the high-pressure homogenizer mechanism largely depends on the type of valve, the pressure applied, the number of passes, the nature of the components and macromolecules, and the food matrix. For this reason, research is needed for each specific program. The results published in the last decade show that HPH is an unnatural technology that can be denied for achieving the goals of the food industry in terms of quality and safety, performance and stability.
What are the characteristics of the best homogeneity:
Four different forms of fat cells in milk
- Single globules unattached.
- Clusters, consisting of two or more spheres that cling freely to clusters.
- Masses, consisting of two or more tightly joined spheres so that the spherical appearance is almost gone Clumps
- Churned or butter particles
A good homogenizer should eliminate all the clusters, masses and butter particles in inhomogeneous valves.
What products should be homogenized
According to the experience of Tekin Machine Radman Company, homogenization or homogenization is an ideal method for the production of emulsions, suspensions and other products that are liquid in liquid. Others (such as water in oil or oil in water) or turning it into small particles are needed. For this reason, the food and beverage industries use this method to produce dairy products, mayonnaise, ice cream, cream liqueurs, salad dressings and more.
Buy a Radman homogenizer or homogenizer
Radman homogenizer or homogenizer of Radman machine is one of the best homogenizers in Iran with high efficiency and durability and made of the best steel material for use in the dairy and juice industries of the country at a reasonable and affordable price.
It should be noted that Radman machine single homogenizer has 1 year warranty and 10 years after-sales service














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.