Search
Product categories
Latest News
Lub pump
technical specification:
| Power: | 10 to 30 w |
|---|---|
| material: | Steel 316 |
| Case: | Steel case |
| Capacity | 1 ton to 100 tons |
| Application | Concentrated and viscous fluids |
| manufacturing | Takin Machine Radman |
Please submit your comments about this product.
Lub pump
Pump lobes, also known as gear pumps and ear pumps, are among the types of positive displacement pumps that work similarly to gear pumps in terms of function and function. The rotation of the lobes or earrings is a non-contact rotation. This means that they have no contact with each other. The maximum flow pumps they support are up to 150 cubic meters per hour and the maximum pressure that can be covered by these pumps is up to 20 bar.
Technical specifications of the pump lobe
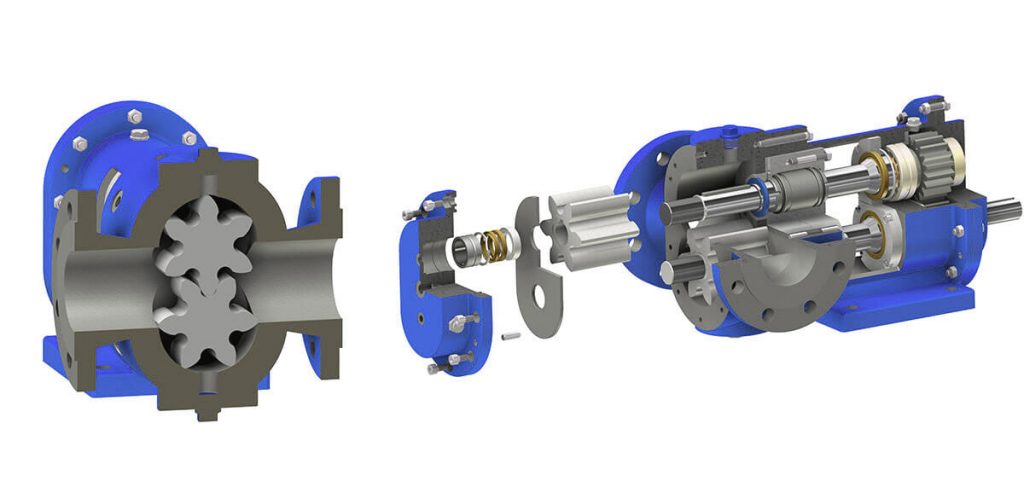
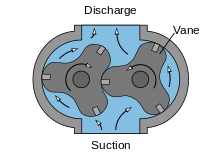
The two pump rotors are connected to a pair of gears that cause the rotation of the pump lobe motor to rotate, where the gears and shaft bearings are not in contact with the fluid and are in a separate chamber from the pumping fluid. The operation of the motor force is such that it enters one of the axes and then is transmitted to the other axle by a gear.
The fluid inside the chamber is divided into two separate parts, one part of the fluid is in the chamber on the suction side, ie the pump inlet, and the other part of the fluid is trapped at the pump outlet or thrust. With the rotation of the rotor, the fluid is directed from the suction part to the thrust and finally to the outlet.
In these pumps, there is no contact between the two rotors and the pump housing, and this causes abrasion between the pump components. The only abrasion in the pump lobe is corrosion of the fluid type or the presence of solid particles in the fluid.
In pump lobes, the ball bearings are located outside the fluid chamber and therefore they have a relatively long length, which will limit the pressure in this type of pump. At start-up, the pump housing must be filled with some fluid. There is an air drain valve at the outlet of the pumps which closes after the pump chamber is filled with fluid.
Hygienic pump or sanitary pump
The lobe pump is in the Hygienic Pump family or the hygienic pump, these lobe pumps can be cleaned without having to separate their connections from their main line. Two important features of Clean in Place, namely washing and cleaning the part in the place where it is installed, and also Sterlize in Place, ie sterilizing in the place of installation without removing the part, are the most important capabilities of lobe pumps.
Non-collision of the lobes of the pump lobes and as a result higher efficiency and more uniformity in the discharge part, as well as the possibility of providing mechanical seal force from the front and its direct design are the obvious and important features of the pump lob.
CIP (Clean in Place) means washing at the installation site and SIP (Sterlize in Place) means sterilization at the installation site are among the capabilities of lobe pumps.
These types of pumps can easily pump fluids such as yogurt, detergents, and other fluids that contain shear sensitivity because they have the least impact on the fluid, both physically and mechanically.
Pump lobes have the ability to pump a wide range of fluids due to the variety of rotor shapes.
The rotor material of the pump lobes is filled with stainless steel or with rubber coating, nylon bronze or PTFE, the type of material is selected according to the work requirements. Rubber coating has anti-wear properties; Nylon Ability to resist hard solids; And bronze reduces the damage caused by momentary overload. PTFE increases the chemical and mechanical resistance of the pump lobe.
Other features of the pump lobe include the ability to pump liquids with high viscosity, with high flow rate and pumping capacity. Due to the internal structure of these pumps, the distance between the gears, and the large chamber they have, allows the pumping of fluids that contain solid particles such as olives and cherries, etc. without damaging them.
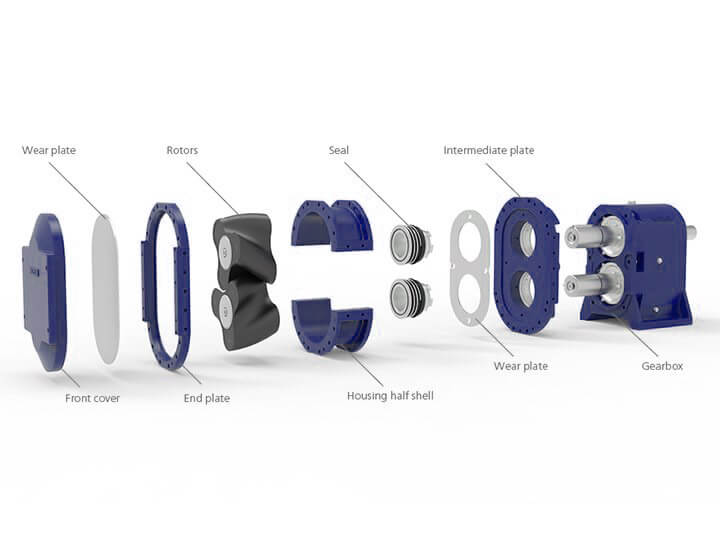
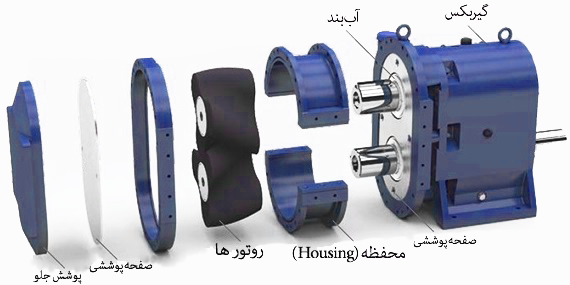
Lob pump components
Main compartment (case or head)
Rotor or Lobe (Gears and Earrings): Rotor pumps can have different structure and design depending on the type of fluid. As a result, the use of the pump lobe is directly related to its design and structure.
Bearings
Leakage or enclosure cap
The lobe structure of the pumps consists of two separate parts:
Components that have no contact with the fluid, such as bearings and gears
Components that come in direct contact with the fluid, such as caps, rotors, pump housings, and seals
Leakage of pump lobe
The end of each shaft entering the fluid is sealed using a mechanical seal or a sealing tape. In cases of greater sensitivity, a double mechanical seal can be used.
Lobe pumping
But how is the flow rate of the pumps determined? The flow of these pumps is directly related to the rotation speed of the rotor. In this way, the higher the speed, the higher the flow rate. However, it should be noted that due to the looseness between the rotors, some of the current in the chamber travels from the high-pressure output area to the low-pressure output area, reducing the output current.
The amount of leakage inside the pump, increasing the pressure difference between the pump outlet and its orifice causes its leakage to increase and this amount of leakage decreases with increasing fluid viscosity. In the pump lobes, the outlet pressure of the fluid is separate and independent of its displacement capacity, and as a result, the outlet pressure can be increased due to the limitation of the pump.
Cavitation phenomenon
Cavitation is the most important reason for limiting the speed of pump pumps. Cavitation phenomenon occurs when in the suction part of this type of pump, when the fluid is sucked in the chamber part, some empty space is created in this area that if there is not enough time to fill this space, cavitation phenomenon occurs. Give. To prevent this from happening, a larger pump must be selected or the engine speed can be reduced.
Cavitation phenomenon
Cavitation is the most important reason for limiting the speed of pump pumps. Cavitation phenomenon occurs when in the suction part of this type of pump, when the fluid is sucked in the chamber part, some empty space is created in this area that if there is not enough time to fill this space, cavitation phenomenon occurs. Give. To prevent this from happening, a larger pump must be selected or the engine speed can be reduced.
Advantages of Pump Lobe
- Hygienic pump or sanitary pump
- Capable of CIP (Clean in Place) and SIP
- (Sterlize in Place)
- Use horizontally and vertically
- Flow without pulse
- Ability to apply sealing force from the front
- Long life
- Do not use accessories
- Ability to make various connections such as; Flange, internal and external gear
- Reduce the effects of human error
- Has a shaft protector in sealing
- Ability to transfer materials in two directions
- Displacement of materials in the form of
- hear and solid-liquid mixtures
- Large space transfer
- Reduce corrosion
- Sturdy body
- Adjustable gear
- Quick and easy installation
- Use different gears
- Seamless suction chamber
Weaknesses of the pump lobe
- In terms of cost and price, lobe pumps are expensive and not very economical
- Lobe pumps require two seals
If the gear adjustment is disturbed, the function of the pump lobe will be disturbed and it will be seriously damaged.
Application of pump lobe
- Resins and coating materials
Distance between gears and high efficiency and uniformity in the discharge section, providing mechanical fluid sealing force from the front and simple and direct design, as well as having the ability to wash at the installation site with water pressure - Shear stress sensitive materials
Due to the fact that it moves sensitive fluids with the least shear force and at low speed and has the ability to move the thinnest materials such as solvents and the most concentrated materials such as polymers. Another important and obvious feature of this product is the addition of a fluid circulation system to control the fluid temperature.
Common uses:
“Repair emulsions, suspensions as well as gels
Flocculant material
Polymers
Waxes and lubricants
Cosmetic creams and ointments as well as lotions
Chemical industry and solvents
Compatibility of transfer of all chemicals with Stainless Steel 316L, systems that require CIP and SIP, as well as fluids that need to be cleaned continuously and intermittently, such as caustic soda.
Normal and common uses:
Resins and coatings
Transfer of play materials and alkalis
Pesticides and herbicides
Soaps and detergents
Food pump lob: Beans, apricots, curds, pickles, fruit pulp, jams, pastes, sauces, puree, shrimp, strawberries, mustard, margarine, cream cheese, buttermilk, mayonnaise, drinks, stews Olive oil, corn oil, buttermilk, jam, jelly, essential oil, cream cheese
Medicinal, cosmetic pump lobes: moisturizing creams, soaps, solvents, toothpaste, vinegar, starch, plasma, varnish, hand cream, lotions, varnish
Pump lobe maintenance
- Leaks in these pumps should be checked periodically and should be replaced immediately if scratches or damage are seen.
- Pump connections must be constantly checked and we must not apply too much force to the pump lobes when servicing them, as the pump lobes are made with great care.
- When production and repair are stopped, all hydraulic and electrical connections are disconnected from the system.
- The fluid that remains in the pump chamber should not solidify and all parts that come in contact with the fluid should be washed after each use.
Due to the fact that the pump lobes work dry for a short time, this drying can damage it and cause a mechanical drop in the pump.
Most use of lobe pumps:
Food industry:
Lobe pumps have been used in the food industry due to their high hygiene standards. High efficiency, simple and easy maintenance, material handling without having to change the shape and nature of materials, and low depreciation are other factors that have led to their use in the food industry.
oil and Petrochemical
Due to their very long life, and the unique features that lobe pumps have, they have been used in the oil and petrochemical industries. In moving materials that have high concentrations such as bitumen, drilling mud, etc., lobe pumps are the best option for choosing a pump.
Water and Wastewater
One of the problems that many water and sewage engineers have to deal with is fluid displacement. Therefore, in water and sewage projects, to move water with different materials such as wood, plastic, stone, etc., drain the flooded areas such as floods or pipe bursts, transfer materials to the treatment plant, move sludge Which have high concentrations, and are generally carried by lobe pumps to move any material with high concentrations.
Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Industries
These pumps have many applications in the agricultural and livestock industry, the most important of which is the transfer of livestock manure to livestock. Due to the fact that animal manure has a high concentration and has materials such as straw, plastic, etc., and such materials can not be moved with ordinary pumps, so these pumps are used to move these materials. Placed. These pumps are also used for spraying liquid fertilizers on agricultural lands. These displacements are done in these pumps with high efficiency.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.